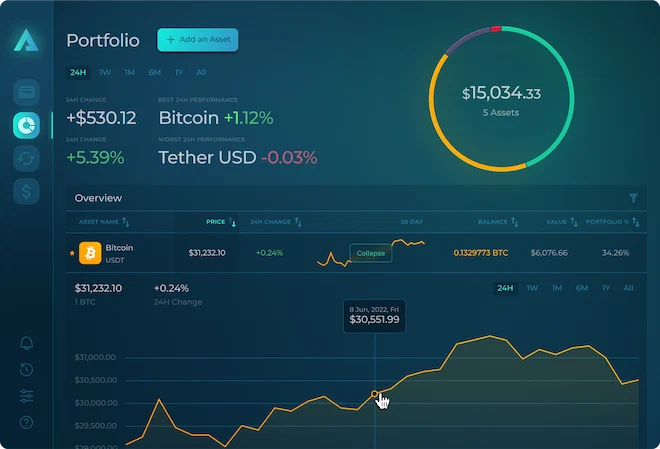









Algorand is a decentralized ledger that uses a pure proof-of-stake consensus protocol. It was created by Silvio Micali, a cryptography expert, and MIT professor, in 2017. The Algorand network is designed to be scalable, secure, and developer-friendly.
The main advantage of Algorand over other blockchain platforms is its scalability. The Algorand protocol can process up to 1,000 transactions per second without sacrificing security or decentralization. This makes it suitable for applications that require high throughputs, such as payments or asset trading platforms.
Another key selling point of Algorand is its security model. Unlike other proof-of-stake systems, Algorand does not rely on validators to secure the network. Instead, it uses a "cryptographic sortition" algorithm that randomly selects block proposers from the pool of token holders. This makes it impossible for any single entity to control the network or 51% attack it.
The token of the Algorand network is called ALGO. It is used to pay transaction fees, participate in consensus, and earn rewards for validating blocks. The total supply of ALGO is 10 billion tokens.